Allergy & Asthma Specialists of KC
Offer a Full Range of Services and Treatments for Children and Adults including:
• Allergic Rhinitis (Hay Fever)
• Sinusitis (Acute/Chronic)
• Allergic Conjunctivitis
• Allergic Asthma
• Non-Allergic Asthma
• Food Allergy (Peanut Immunotherapy)
Frequent Infections: Understanding Why They Happen and What To Do
A specially formulated liquid placed under the tongue.
They are an alternative to allergy shots which is especially helpful for children, teens, and patients who fear needles. If your schedule does not allow office visits for allergy shots or you travel or live far away; allergy drops are the right choice for you
Find out if you’re a candidate for allergy drops, by clicking here to schedule an appointment.
Do you find yourself battling one infection after another?
While occasional infections are normal, experiencing them frequently can disrupt your life and may indicate an underlying issue.
What Might Cause Frequent Infections?
Several factors can contribute to a weakened immune system and an increased susceptibility to infections:
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain chronic illnesses like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, autoimmune diseases (such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis), and cystic fibrosis can impair immune function.
- Medications: Some medications, including corticosteroids, chemotherapy drugs, and immunosuppressants used after organ transplantation, can suppress the immune system.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor nutrition (lacking essential vitamins and minerals), chronic stress, inadequate sleep, and lack of physical activity can all weaken the body's defenses.
- Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders (PIs): These are genetic disorders where parts of the immune system don't function properly. There are many different types of PIs, ranging from mild to severe.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain toxins or pollutants over time might impact immune function.
- Age: Very young children and older adults often have immune systems that are either still developing or naturally weakening, making them more prone to infections.
- Surgical Procedures or Invasive Treatments: These can sometimes increase the risk of infection, especially if the immune system is already compromised.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Deficiencies in specific nutrients like zinc, iron, vitamin C, and vitamin D can affect immune cell function.
Common Symptoms Associated with Frequent Infections
The symptoms will vary depending on the type of infection, but some common signs of frequently occurring infections include:
- Recurrent colds or flu-like illnesses: Experiencing these multiple times a year, often with severe or prolonged symptoms.
- Sinus infections (sinusitis): Repeated episodes of nasal congestion, facial pain, and discolored mucus.
- Ear infections (otitis media): Frequent ear pain, fluid drainage, and hearing difficulties.
- Bronchitis or pneumonia: Repeated chest infections with coughing, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
- Skin infections: Boils, abscesses, or cellulitis that occur often.
- Yeast infections or thrush: Persistent or recurring fungal infections.
- Slow wound healing: Minor cuts or scrapes taking an unusually long time to heal.
- Swollen lymph nodes: Persistent or frequently enlarged lymph nodes.
- Fatigue: Persistent and unexplained tiredness.
- Fever: Recurrent or low-grade fevers without a clear cause.
Evaluation of Frequent Infections
If you are experiencing frequent infections, it's important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause. The evaluation may involve:
- Detailed Medical History: Your doctor will ask about your infection history, family medical history, current medications, lifestyle, and any other relevant health conditions.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical exam to look for signs of infection or underlying conditions.
- Blood Tests: These can help assess overall immune function, identify specific antibody levels, check for signs of inflammation, and screen for underlying medical conditions like diabetes or HIV. Specific tests for immune cell counts (like lymphocytes) and function may be ordered.
- Urine Tests: To check for urinary tract infections and assess kidney function.
- Imaging Studies: Depending on the type of recurrent infections, X-rays, CT scans, or other imaging may be used to evaluate the affected areas (e.g., lungs for pneumonia, sinuses for sinusitis).
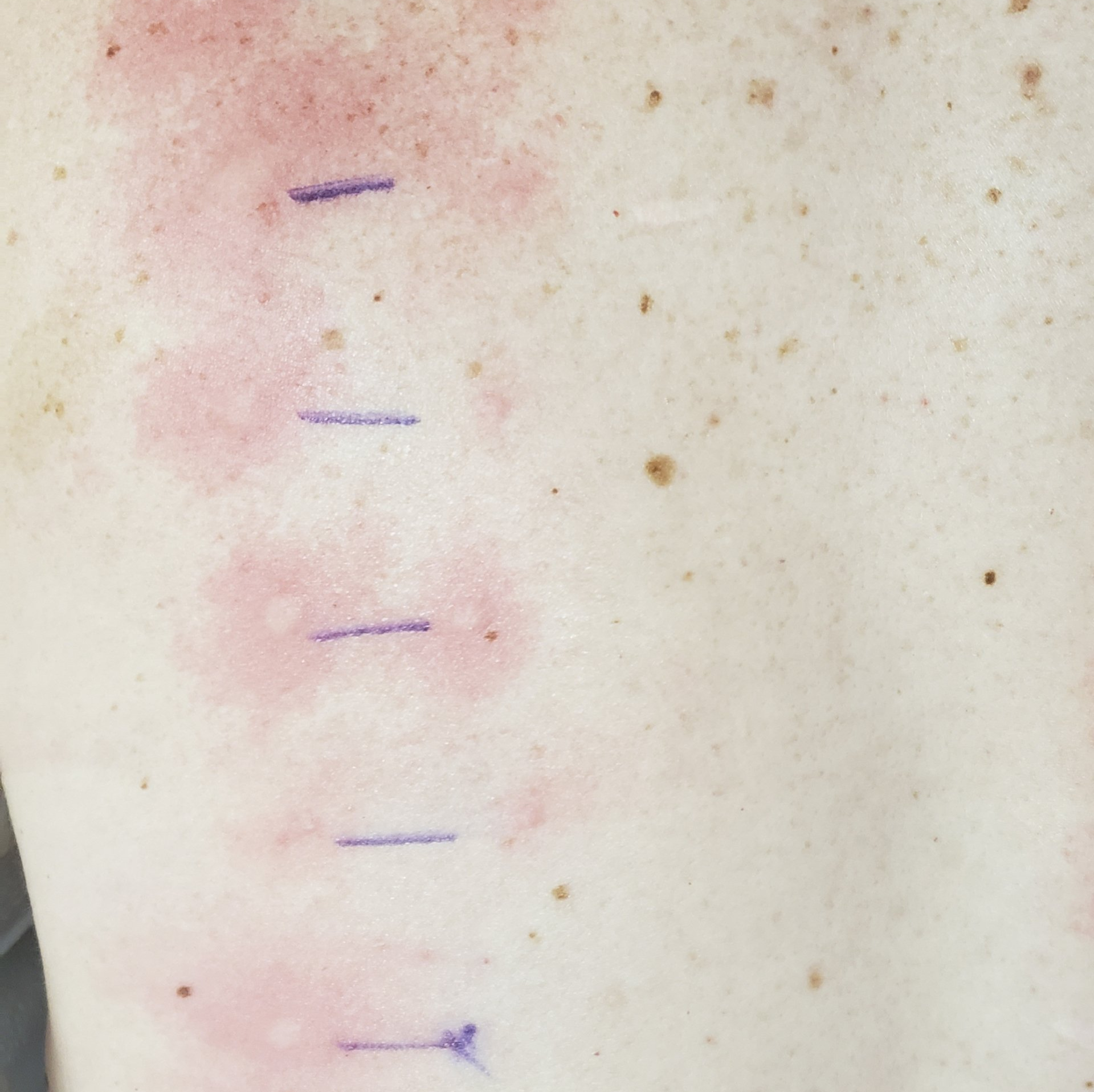
- Allergy Testing: In some cases, allergies can contribute to frequent respiratory infections.
- Immunoglobulin Levels: Measuring the levels of different types of antibodies (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE) can provide insights into immune function.
- Genetic Testing: If a primary immunodeficiency disorder is suspected, genetic testing may be recommended.
- Referral to a Specialist: Depending on the findings, your primary care physician may refer you to an infectious disease specialist or an immunologist for further evaluation and management.
Treatment Strategies for Frequent Infections
The treatment approach for frequent infections will depend entirely on the underlying cause:
- Addressing Underlying Medical Conditions: Effectively managing conditions like diabetes or autoimmune diseases is crucial for improving immune function.
- Medication Management: If medications are contributing to immune suppression, your doctor may adjust the dosage or explore alternative treatments when possible.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, regular exercise, 1 sufficient sleep, and stress management techniques, can significantly support the immune system.
- Nutritional Support: If nutrient deficiencies are identified, supplementation with vitamins and minerals may be recommended under medical guidance.
- Vaccinations: Staying up-to-date on recommended vaccinations can prevent many common infections.
- Preventative Medications: In some cases, such as for individuals with certain primary immunodeficiencies, prophylactic antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed to prevent infections.
- Immunoglobulin Therapy: For some primary and secondary immunodeficiencies, intravenous or subcutaneous immunoglobulin (IVIG or SCIG) therapy can provide the body with the necessary antibodies to fight off infections.
- Treatment of Active Infections: Prompt and appropriate treatment of each infection with antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals is essential to prevent complications.
- Management of Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders: Treatment for PIs varies widely depending on the specific disorder and can include bone marrow transplantation, gene therapy (in some cases), and lifelong immunoglobulin therapy.
If you are concerned about frequent infections, seeking medical evaluation is the first and most important step towards identifying the cause and developing an effective management plan.